The Desmoid Tumor Is A Rare, Noncancerous Tumor That Can Be Locally Invasive And Cause Significant Morbidity
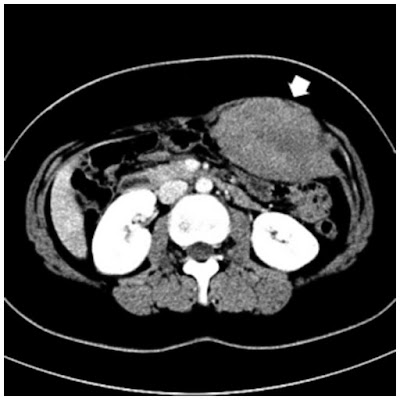 |
| Desmoid Tumor |
Connective tissue
growths known as Desmoid Tumors are
benign. Arms, legs, and the belly are the areas where desmoid tumours often
form. The term "aggressive fibromatosis" is also used to describe
desmoid tumours. Some desmoid tumours grow slowly and might not require
immediate treatment. Others are treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy,
or other drugs because of their quick rate of growth.
For instance, Iterion Therapeutics announced in June 2022 that results from a Phase 1 study of tegavivint in patients with Desmoid Tumors would be highlighted in a poster presentation and discussion session at the 2022 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting (ASCO 2022), a meeting for conducting scientific events for oncology experts, patient advocates, and other interested parties.
According to Coherent Market Insights, Global desmoid tumors market is estimated to be valued at US$ 2,494.1 million in 2022 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 7.3% during the forecast period (2022-2030).
Desmoid Tumors, also known as aggressive fibromatosis, are rare, noncancerous tumors that grow from the connective tissue in the body. Desmoid tumors can occur anywhere in the body, but they are most commonly found in the abdominal wall, shoulders, and thighs. They are often slow-growing, but they can be aggressive and invade surrounding tissues, causing significant morbidity and even mortality.
Desmoid tumors are not cancerous, but they are often
classified as intermediate tumors because they have the potential to invade and
cause damage to surrounding tissues. They are also known as
"borderline" tumors because they are somewhere between benign and
malignant. Desmoid Tumors are different from other types of
tumors because they do not metastasize, or spread to other parts of the body,
but they can be locally invasive.
The cause of desmoid tumors is not well understood, but they
are thought to be caused by mutations in the APC gene, which is also associated
with a hereditary condition called familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). FAP is
an inherited disorder that causes the growth of thousands of polyps in the
colon and rectum, and individuals with FAP have an increased risk of developing
desmoid tumors.
Therapy that kills cancer cells by exposing them to a
radioactive material that emits an alpha particle, a form of high-energy
radiation. After being injected into a vein, the radioactive material travels
through the blood and gathers in specific bodily tissues, such as cancerous
bone tumours. This kind of radiation might harm neighbouring healthy tissue
less. The use of Alpha
Emitter radiation therapy in the treatment of prostate cancer
that has metastasized to the bone is now under investigation.
Desmoid Tumors are most commonly diagnosed in young
adults, with a peak incidence between the ages of 25 and 35. They are more
common in women than in men, and they are more commonly found in individuals
with a history of FAP or a family history of desmoid tumors.



Comments
Post a Comment