Transfusions Of Blood And Blood Components Are Used To Save The Lives Of Patients Suffering From Bleeding Disorders
 |
| Blood And Blood Components |
Blood is a fluid composed of
plasma and cells that circulates throughout the body. It provides essential
substances to cells and organs, such as sugars, oxygen, and hormones, and
removes waste from cells. Hematologists investigate and treat blood and bone marrow
disorders. They also research and treat diseases of the immune system, blood
clotting, and blood vessels. Blood-related health problems can be fatal, but
effective treatment is often available. Blood diseases, mostly different types
of anaemia, were responsible for 10,066 deaths in the United States in 2008.
Blood
And Blood Components are used in clinical settings for blood
transfusion to save the lives of patients suffering from bleeding disorders,
traumatic surgery, chronic diseases, or rare blood diseases. Hemophilia A or B,
sickle cell anaemia, Von Willebrand disease, and other bleeding disorders
necessitate blood transfusions. Patients who have been severely injured in car
accidents or other traumatic incidents such as violence and assault usually
require traumatic surgery. Road accidents cause significant blood loss and
haemorrhage, necessitating an immediate blood transfusion to maintain blood
volume and save the patient's life.
Furthermore, blood transfusion is
required in the treatment of chronic diseases such as blood cancer because
cancer treatment involving surgery causes significant blood loss and blood cell
loss. Patients undergoing stem cell transplantation for the treatment of blood
cancers such as leukaemia, myeloma, lymphoma, and others require high doses of
chemotherapy, which causes blood cell depletion. Furthermore, plasma donation
is critical for maintaining immunoglobulin levels in the body, which are
required for the immune system to function properly.
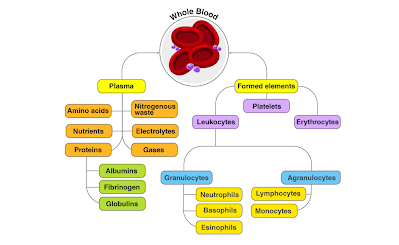
The main of blood Components are:
·
Plasma -
In humans, plasma accounts for approximately 55% of blood fluid. Plasma is 92%
water, with the remaining 8% consisting of:
glucose, Mineral salts, fats, and vitamins
·
Red Blood
Cells- The shape of red blood cells is a slightly indented, flattened disc.
They are responsible for transporting oxygen to and from the lungs. Hemoglobin
is an iron-containing protein that transports oxygen to its destination. A red
blood cell has a four-month lifespan and is replaced on a regular basis by the
body. Every second, the human body generates approximately 2 million blood
cells.
·
White
Blood Cells- White blood cells constitute less than 1% of blood volume and
serve as vital defences against disease and infection. White blood cells in a
microliter of blood typically range from 3,700 to 10,500. Increased or
decreased levels of white blood cells can indicate disease.
·
Platelets-
Platelets work with clotting proteins to stop or prevent bleeding.
Platelets should range between 150,000 and 400,000 per microliter of blood.



Comments
Post a Comment