Waste-To-Energy Plants While Aiding To Boost Energy Production Contribute To Carbon Emission
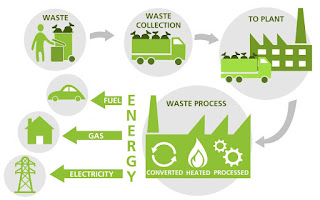
Waste-To-Energy is the procedure of converting waste to energy in the form of heat and/or electricity. It involves the use of heat exchangers, in order to convert solid waste to gas, liquid fuel, and eventually electricity. In other words, it is an efficient process to use waste materials in generating electricity at a lower cost. Waste-To-Energy is increasingly being used worldwide as an effective means of reducing landfill wastes, and as a useful source of renewable energy. Waste-to-energies are also being used to create hydrogen for electrolysis, thus, providing an environmentally friendly way to generate electricity.
Waste-to-electricity plants have several advantages over traditional power plants. Waste-to-electricity plants can produce clean energy that is free from all the hazardous by-products of traditional electricity generation. Another advantage is that the generated electricity is eco-friendly. This is because less fossil fuels are consumed and thus, less carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere. A third advantage is that a waste-to-electricity plant does not pollute the air. However, trash-burning facilities increase CO2 emission. For years, several European countries such as the U.K and Germany have supported “Waste-To-Energy” incinerators as they help in minimizing pollution and boost energy production. However, these incinerators also increase CO2 footprint in the environment.
Waste-to-electricity is one of the most important solutions to the growing concerns about waste disposal and the shortage of non-renewable energies. Waste-to-electricity systems can be created in many forms, depending on the waste material involved and the available technologies for energy production. There are two common processes, where electricity is produced by combustion of waste in burning engines; and, there are others, where energy is generated through energy conversion of waste materials. The more common waste-to-electricity process, where solid waste is converted to energy, is commonly known as combustion energy.
The combustion process is the most commonly used energy producing process in many countries. This method involves injecting fuel into the combustion chamber with the help of fuel gas, air or water. Oxygen is provided with the help of reaction between fuel and oxygen. Waste, which is solid, is allowed to enter into the chamber and solidify, while the inert gases are allowed to come out of solidify and get mixed with the fuel gas. The resulting product is heat energy.
The second process is known as heat-to-electricity energy conversion. In this process, waste materials are broken down into simple compounds like hydrogen, which are a powerful energy carrier, and oxygen, which is effective carriers of other forms of energy like electricity. This type of process also takes care of the waste products, which do not dissolve in water. It uses the principles of submersion for gasification of solid waste and oxidation of oxidized metals. Heat generated electricity is produced by the use of this process.
See Full Report@ https://bit.ly/3jmDQIr



Comments
Post a Comment